Free Crypto Course Session 4: Decentralised Finance, Banking and Crypto Regulations

Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
Decentralised finance, or DeFi, tries to re-create conventional financial instruments by removing intermediaries through technology.
Key Points
- Decentralised finance uses blockchain technology to offer traditional financial services.
- In DeFi, blockchain expands its uses from simple transactions to more complex services.
- You might have heard the term “Open Finance” before, which was the first aim to implement the concept of DeFi.
- Most DeFi applications are built on the Ethereum blockchain, the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency platform.
DeFi vs. Traditional Finances
DeFi
You are the sole owner of your money
You control where your money goes and how it’s spent.
Transactions happen within minutes
Your activity remains pseudonymous
Open 24/7
It is built on transparency
Traditional Model
Your money is held by a company or third party
You have to trust the bearer of your money
Transactions are partially processed manually, which delays them.
You might be denied certain financial services due to your origin, identity, etc.
Financial institutions are closed books
Most Popular DeFi applications
- Decentralised exchanges (DEXs): Users are connected directly with one another, there is no need for intermediaries in order to exchange money.
- Lending platforms: Lenders and borrowers of cryptocurrencies are connected via smart contracts.
- “Wrapped” bitcoins (WBTC): A way of sending bitcoin to the Ethereum network so the bitcoin can be used directly in Ethereum’s DeFi system.
- Prediction markets: Betting markets for future events, such as elections. The goal is to create reliable predictions, without interference of intermediaries and/ or manipulations.
Defi and Ethereum
- DeFi runs in the Ethereum Blockchain.
- Ethereum’s platform uses smart contracts, which execute transactions automatically when certain predetermined conditions are met.
- No one owns Ethereum or the smart contracts that live on it.
- Since most of Ethereum’s products will never take custody of your funds, it allows complete financial freedom, leaving you in control.
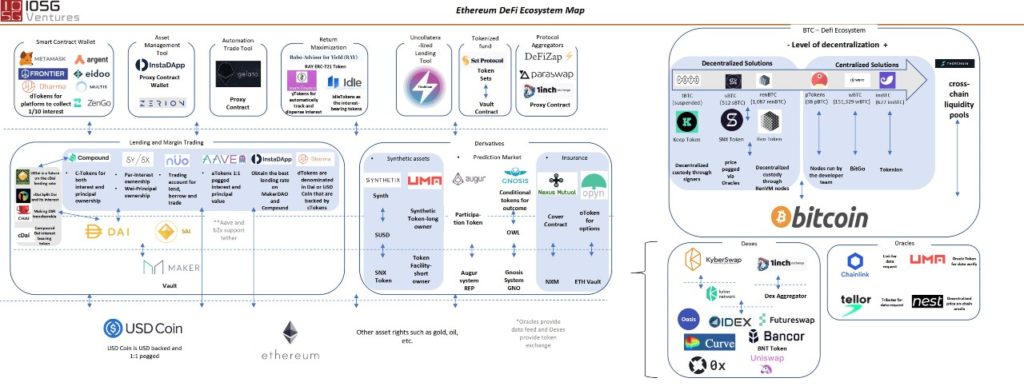
Source: Reddit
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is self-executing piece of code that enforces transactions verifiable on the Ethereum blockchain.
Key Points
- Smart contracts are a key element of the Ethereum network and essential for the blockchain.
- Most of the contractual clauses are, partially or fully, self-executing, self-enforcing, or both.
- The main goal is to provide a superior security and a cheaper alternative to traditional contractual laws.
- These contracts are autonomous, decentralised and transparent, meaning they are irreversible and unmodifiable once deployed.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
Initial Coin Offerings (ICO) are a popular fundraising method used primarily by crypto and blockchain startups.
Key Points
- It’s usually launched by a crypto company looking to raise funds to create a new coin, app, or service.
- Supporters of the project buy some of the project’s tokens (coins) with fiat- or digital currency in exchange of the newly-created coins.
- It works similarly to a company shares sold to investors during an Initial Public Offering (IPO).
- As in any investment, some ICOs have yielded massive returns for investors but others have turned out to be a fraud or have failed.
- ICOs differ from crowdfunding in that crowdfunding is mainly done from donations, while the backers of ICOs are motivated by a prospective return on their investments.
- ICOs are also called “crowdsales.”
- Since ICOs are, mainly, completely unregulated, investors need to do research and be cautious when investing in new coins.
- The best way to stay ahead of new ICOs is to stay informed and follow the latest news.
Banking
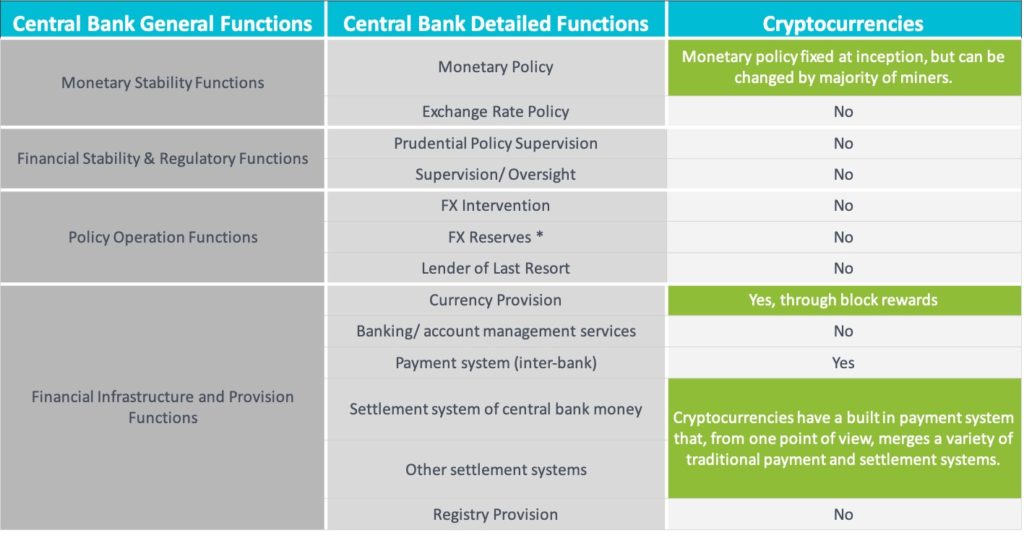
Central Banks vs. Cryptocurrencies
- In each country there is a financial entity that defines and supports the monetary system of their nation. That is a central bank.
- The most common functions handled by Central Banks are: monetary stability, financial stability, regulation, policy operations management and financial infrastructure provisioning.
- Since cryptocurrencies are not issued by a state (or central bank), they are not considered legal tender.
- Most of cryptocurrencies provide a very light set of central banking functions like setting monetary policy, payment/transfer services and issuance/distribution of new ‘coins’/units.
Central Bank Digital Currency
Digital currency issued by a central bank
Key Points
- Central bank digital currencies (CBDC) are also known as digital fiat currencies.
- CBDC is aimed to be a high-security digital instrument.
- It is a means of payment, a unit of account, and a store of value, just like normal currencies.
- Like paper currency (or coins), each unit of CBDC is uniquely marked to prevent counterfeit.
- Currently most central banks are looking into digital currencies, which CBDCs mostly remaining in the hypothetical stage.
- China issued the first ever digital currency, done by a major economy, the digital RMB.
Cryptocurrencies vs Central Bank Digital Currency – Key Differences
- The main difference is the governance: a CBDC is centrally controlled, whilst cryptocurrencies use a blockchain or other distributed ledger technology.
- CBDC does not use blockchain technology
- Like any third party-controlled digital asset, the main risk of CBDCs is that the issuer/ authority of the Central Bank Digital Currency can manipulate, add or remove money from anyone’s account remotely with the flip of a switch.
- Cryptocurrencies are protected against this kind of threat by ensuring that more than 50% of the mining power is in agreement before proceeding with any action.
Crypto Regulations
Key Points
- For a currency to be considered legal tender, it has to be recognised by another nation-state, preventing cryptocurrencies to be formally recognised as currency.
- Even if it’s not a currency for legal purposes, cryptocurrencies almost certainly are property /assets instead.
- In 2013, The U.S. Treasury classified bitcoin as a “convertible decentralised virtual currency”.
- In September 2015, it as was also classified as a commodity by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, CFTC.
- Per IRS, bitcoin is taxed as a property.
United States of America
- According to IRS – “virtual currency” is considered property for tax purposes.
- Buying cryptocurrency with USD is not a taxable event.
- Income and expenses generated in cryptocurrencies are taxed and as per regular standards.
- Crypto earned through mining is treated as ordinary income. i.e. you have to report the value at the time you are awarded the coin.
- Keep and eye on Wyoming (Caitlin Long – LN) ‘#Wyoming will recognize #DAOs as a new type of LLC, effective July 1!’
European Union
- In 2014 bitcoin was classified as a convertible decentralised virtual currency by the European Central Bank (ECB).
- Since a regulatory regime was still not in place, the European Banking Authority advised European banks not to deal in virtual currencies just yet.
- In 2015 it was dictated that VAT/GST is not applicable to the conversion between traditional fiat currency and bitcoin.
- As of 2020 Crypto exchanges and wallet providers must be under the “Anti-Money Laundering Directive”.
- Small European nations such as Malta, Cyprus, Austria and Estonia, are embracing new technological trends and pacing the future of blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
EU – Malta
- Cryptocurrencies are recognised by the government as “a medium of exchange, a unit of account, or a store of value”, but not as legal tender.
- The financial regulator in charge of cryptocurrency exchanges in Malta is the Malta Financial Services Authority, or MFSA.
- There is no specific cryptocurrency tax legislation, nor is VAT applicable to transactions exchanging fiat currency for crypto.
- Three new laws are enabling blockchain based businesses: The Malta Digital Innovation Authority Bill, The Technology Arrangements and Services Bill and the Virtual Financial Assets Bill.
- The Malta Gaming Authority has expressed interest in integrating and allowing the use of cryptocurrencies by MGA licensees.
Key Regulatory Timestamps
- 2018: parliament passed three bills establishing a comprehensive regulatory foundation for blockchain and digital currencies.
- Malta is promoted as the “Blockchain Island”
- 2020: With only 26 of the initial 83 companies applying for licence, and none granted to date, all signs point to the fact that many entities found the VFA’s requirements too demanding.
Malta – Notable Blockchain Companies (with hesitation)
- Binance / Binance Labs: Established in 2017, Binance is a global-reaching digital currency exchange. It is also maintaining its own digital currency BNB and proprietary blockchain. Binance is no longer based in Malta as of today (year 2021)
- Pacific: Pacific offers a blockchain-powered payments system for social media and e-commerce that utilises smart QR codes.
- Changelly: Changelly is a popular crypto-exchange that allows for the purchase and exchange of more than 150 digital currencies and digital assets.
- Komodo Platform: Komodo Platform is a popular and open smart-chain platform built on a multi-chain architecture.
- BitPay: Established in 2014, BitPay is a digital currency and digital assets exchange.
- Chillz: Fan Tokenisation
- Stobox: Stobox, which was founded in 2018, is a platform enabling small and medium-sized businesses to issue digital securities.
Other European Territories
- Slovenia: Mining and businesses selling goods/ services in bitcoin are taxed.
- Switzerland: Bitcoin businesses may need a banking licence and are subject to anti-money laundering regulations.
- Norway: Bitcoin is an asset and falls under the sales tax regulation.
- Sweden: Subject to Financial Supervisory Authority regulations and treated as currency exempt of VAT.
- Germany: “Unit of account” and can be used for tax and trading.
- Russia: The use of other currencies beside the Ruble, is illegal. Crypto is considered a high risk asset.
United Kingdom
- For the purpose of taxation, crypto assets are considered property.
- A capital gains tax (CGT) liability may become due if a gain is made on disposal.
- The CGT threshold for UK taxpayers is £12,300 per tax year, as at 6 Apr 2020.
- Airdrops and forks are mentioned in the guidance.
- Much like shares, crypto assets can be pooled.
Central and South America
- Argentina, Brazil and Chile: bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are legal, but unregulated.
- Bolivia: Bitcoin activities were banned by the Central Bank of Bolivia in 2014. 60 cryptocurrency promoters were arrested in May 2017
- Ecuador: The government banned bitcoin and other cryptocurrency activities in 2014, however use of Bitcoin still grows until now.
- El Salvador: In 2021, El Salvador becomes the first country to adopt bitcoin as currency.
Asia
- Lebanon and Jordan have issued warnings on the use of Bitcoins, but it is still legal.
- Japan recognises cryptocurrencies as a method of payment.
- Singapore recognises cryptocurrency transactions as barter sales for tax purposes
- Crytpotocurrencies are illegal in Kyrgyzstan and Bangladesh
- India bans the purchases/ sales of crypto but expressed believe in blockchain technologies
- In early January 2018, China took a hostile position for local miners. This hostility has continued and during the year 2021, the government has shown a very negative approach towards crypto.
Connecting Blockchain & Crypto Companies
Quantum Supremacy
Quantum supremacy, or quantum advantage, is the idea that a computer based on quantum physics can solve a problem in record time, something that no conventional computer could do in a reasonable amount of time.
Key Points
- Quantum computing wants to utilise the “all possible directions” idea in order to get lots of computations done in parallel, at the same time.
- Google claims that their quantum computer has completed a computation in a couple of seconds, compared to thousands of years for a regular computer.
- Quantum computing challenges blockchain speed, which is know to be notoriously slow
- Challenges PoW/PoS
- It is currently in its early stages of research
- Vitalik (Ethereum) resists it for now
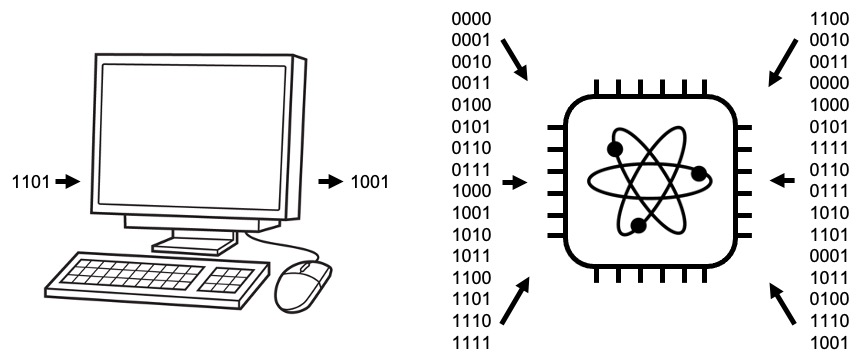
Quantum Computing
- Traditional computers use 1 and 0 to break through operations, quantum computers, on the other hand, use quantum bits or qubits.
- The special particularity of qubits is that they have a third state called “superposition”, which allows them to represent a 1 or a 0 at the same time.
- With the superposition, a quantum computer allows two qubits to represent four scenarios at the same time.
Normal Computer vs Quantum Computer
A.I.
Artificial intelligence uses computers to mimic human intelligence. AI models differentiate themselves from traditional computers, as they “learn! by improving as they are fed with new data. Like a human brain, an AI model can be developed and improved.
A.I. Uses on Blockchain
- Artificial Intelligence models can be used to analyse, classify and make predictions from the information fed to them (data).
- Blockchain allows for collaborative and secure data sharing since information can’t be altered once stored in the blockchain.
- This translates into more authentic and close-to-reality results.
- In order for AI models to remain effective and updated, their database needs to be filled with quality information. Unfortunately, the amount of data on the internet is not always trustful.
- Machine learning is a subdivision of artificial intelligence and it is used to extract insights from data.
- In general, larger (and better) datasets help create more efficient machine learning models.
Practical Example of AI and Blockchain
- At the doctor’s office, the AI assistant, that is expertly trained, has ingested millions of medical periodicals to this date.
- It would not be humanly possible for any doctor to keep up with all the latest medical breakthroughs and advances.
- Important question: who provides the training to this AI Doc?
- Professional, unbiased and reliable training is key
- If, for example, it’s been trained by one Big Pharma company, it wouldn’t be reliable.
- Blockchain technology ensures objective and unaltered training.

Photo by Possessed Photography on Unsplash
IoT (Internet of Things)
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical internet – connected devices and capable of collecting and transmitting data without the need for human interaction.
The IoT Network
- All our electronic devices are fitted with chips, sensors, etc, each transmitting data to the IoT network.
- Security has always been a major concern, that has hindered the large-scale deployment of IoT.
- Vulnerable IoT devices make it easier for cybercriminals to target them.
- The existing centralised systems that authenticate, authorise and connect different nodes won’t be able to keep up with the ever growing network of IoT devices. Blockchain and its decentralised network, will help alleviate that burden.
How can Blockchain help IoT?
- IoT security and scalability challenges can be addressed with blockchain technology.
- By eliminating the single point of control, you also eliminate the single point of failure. Blockchain doesn’t allow one organisation to control the data generated by the IoT.
- The idea is to give each device, at their creation point, an identity (chip, serial number, etc) that allows the device to be tracked and verified throughout their whole lifecycle within the Blockchain.
- With blockchain technology, transactions can be coordinated in a fraction of the time among billions of devices.
Applications of IoT and Blockchain
- Freight transportation
- With blockchain, temperatures, position, arrival times and shipping status of containers can be continuously be tracked as they move.
- Component tracking and compliance
- For safety and regulatory purposes, components can be tracked as they go into an aircraft, automobile, or other products is critical for both safety and regulatory compliance.
- Log operational maintenance data
- Critical machines can be tracked for their safety and maintenance if connected to the blockchain.
Big Data
Big Data is a large amount of data that traditional databases can’t capture, manage, or process because of its size or type.
Key Points
- Big data is composed of structured, semistructured and unstructured data collected by organisations and companies for information and/ or other advanced analytics applications.
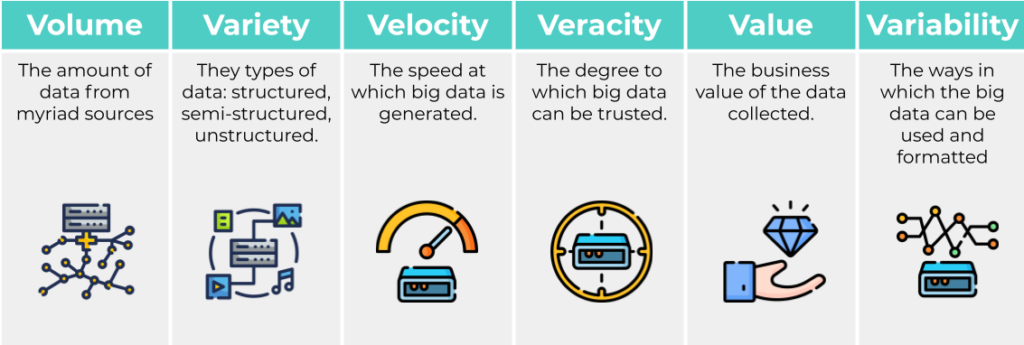
- Big data is often characterised by the 6Vs:
- Volume: large volumes of data
- Variety: wide variety of data types
- Velocity: the speed at which the data is generated, collected and processed.
- Veracity, value and variability are the other key characteristics.
Key Points
- Big data is mainly used to improve operations, provide better customer service, create personalised marketing campaigns and increase profitability.
- Big data can come from many different sources, mainly through the IoT devices and other, more traditional methods, such as business transaction systems, customer databases, medical records, internet clickstream logs, mobile applications, social networks, etc.
Big Data and Blockchain
- Blockchain adds another security layer to the Big Data analytics process.
- Blockchain-generated Big Data is
- Safe: it cannot be manipulated or altered.
- Valuable: it is structured, abundant and complete.
- “If Big Data is the quantity, blockchain is the quality”
Forbes’ Blockchain Key Leaders

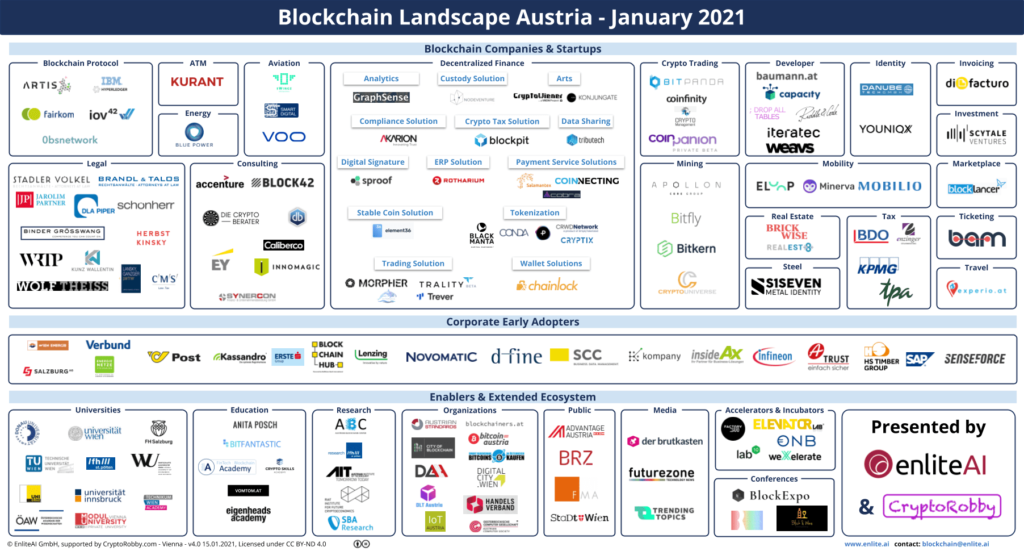
Source: enlite.ai
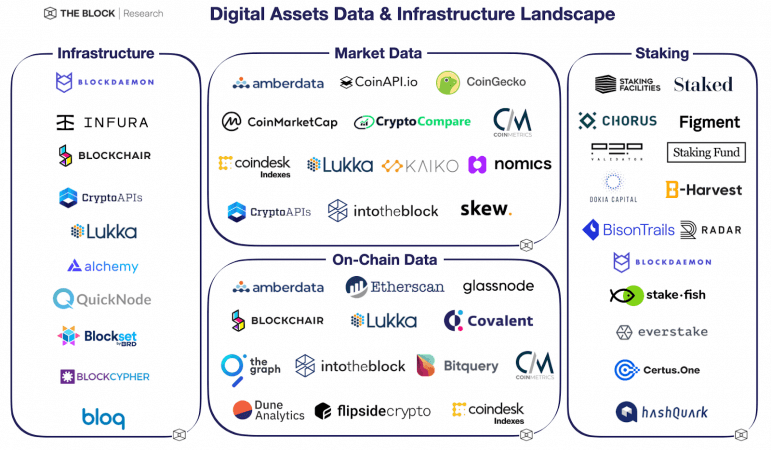
Source: The Block