Free Crypto Course Session 3: Altcoins & Crypto Services

Altcoin Definition
Altcoins are all other alternative cryptocurrencies other that are not bitcoin.
Key Points
- An “alt-coin” is a form of payment that is based on the basic concepts of Bitcoin but differs or improves in its execution.
- Many people have developed their own “alt – currencies,” with their own laws and networks.
- Some older concepts, such as Ripple, have been enhanced by blockchain innovation and have grown into their own entities.
- While some are minor tweaks to the Bitcoin protocol with a small audience, others are intriguing sources of innovation.
- Although Bitcoin is the king, several alt-coins have received a lot of acceptance.
- These new coins have different attributes and generate their own blockchains that are independent to the Bitcoin blockchain, using the original open source software with a few modifications.
Best Known Altcoins
- Currently more than 5,000 altcoins
- Some of the best-know coins are: Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), Cardano (ADA), Polkadot (DOT), Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Stellar (XLM), Chainlink, Binance Coin (BNB)
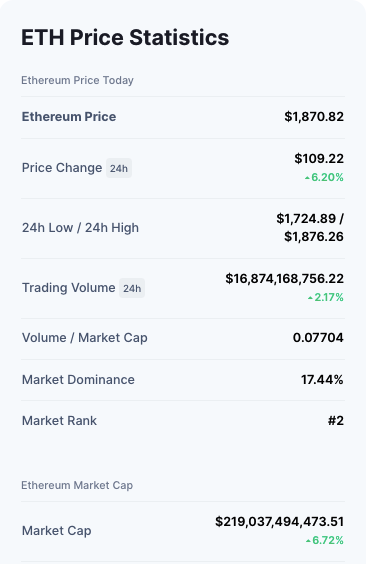
Ethereum (ETH)
- Ethereum is one of the most popular and globally founded projects.
- Ethereum’s goal is to establish a decentralised range of financial opportunities that anyone in the world, regardless of nationality, ethnicity, or beliefs, can use for free.
- The Ethereum blockchain may run any decentralised application’s programming code.
- Rather than having to create a new blockchain for each new application, Ethereum allows developers to create several applications on a single platform.
- Ether is the cryptocurrency of Ethereum. It is mined and fuels the network.

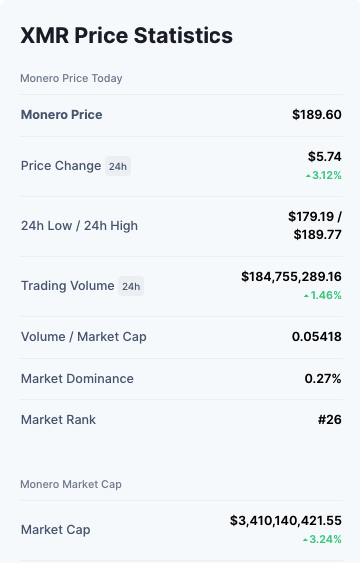
Monero (XMR)
- Monero saw the light in 2014, initially as a fork of Bytecoin.
- Monero allows its users to select to selectively disclose their transactional history to selected parties.
- It has always focused on providing strong privacy while offering optional transparency.
- Monero has a dynamic fee mechanism and a changeable block size.
- It employs an encrypted public ledger, which allows anyone to send or record transactions while keeping the source, amount, and destination hidden from outside observers.

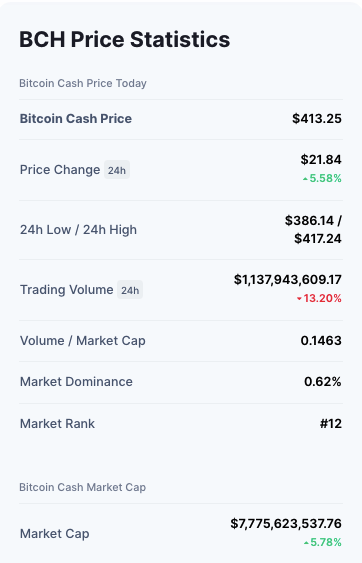
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
- Bitcoin Cash was created as a result of a fork from Bitcoin.
- It was established in 2017
- This blockchain’s block size is 8 MB.
- Miners can earn more transaction fees if there are more transactions in a block.
- Approximately 2 million transactions may be handled each day, compared to 250k transactions per day for Bitcoin.
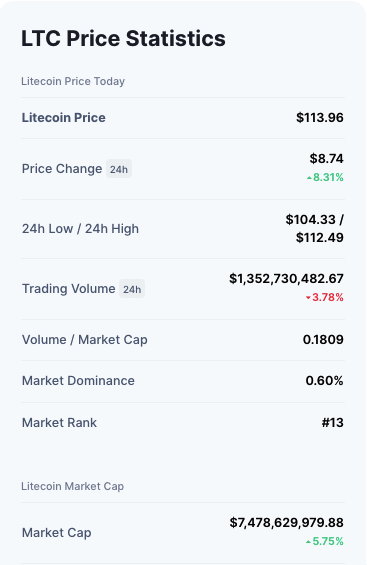
Litecoin (LTC)
- Litecoin is an open-source software project and a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency.
- Starting in October 2011, it was an early bitcoin spinoff or cryptocurrency.
- Litecoin is nearly identical to Bitcoin.
- In comparison to Bitcoin’s 10 minutes, the Litecoin Network promises to process a block every 2.5 minutes.
- As a result, Litecoin can confirm transactions significantly more quickly than Bitcoin.

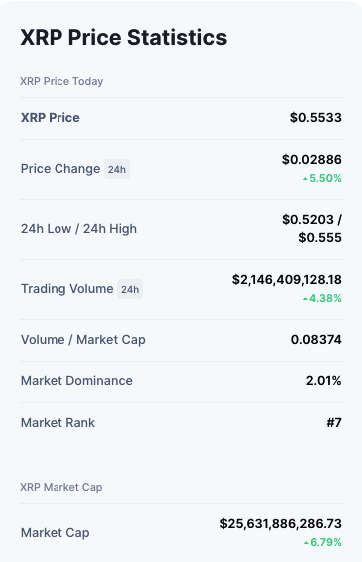
Ripple (XRP)
- Ripple is a distributed open source protocol that supports tokens representing fiat cash, bitcoin, commodities, or other units of value such as frequent flier miles or mobile minutes.
- It was launched in 2012 and is based on a distributed open source protocol.
- Ripple claims to be able to facilitate “secure, instantaneous, and almost free worldwide financial transactions of any size with no chargebacks.”
- The native cryptocurrency of the Ripple Ledger is XRP

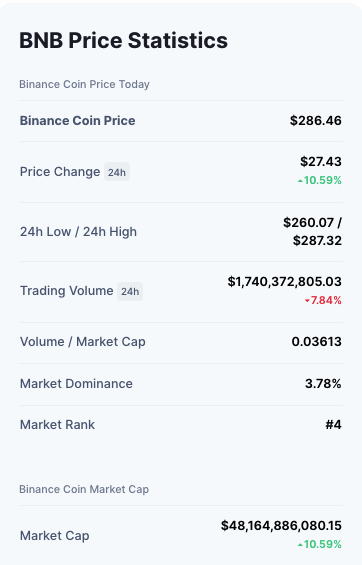
Binance Coin (BNB)
- Binance Coin (BNB) is a the official cryptocurrency of the Binance crypto exchange.
- Binance Exchange is one of the most popular crypto exchanges in the world,
- Binance accepts and trades other major cryptocurrencies like, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, etc.
- BNB was launched in 2017 and worked with the ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain before becoming the native currency of Binance’s own blockchain, the Binance Chain.

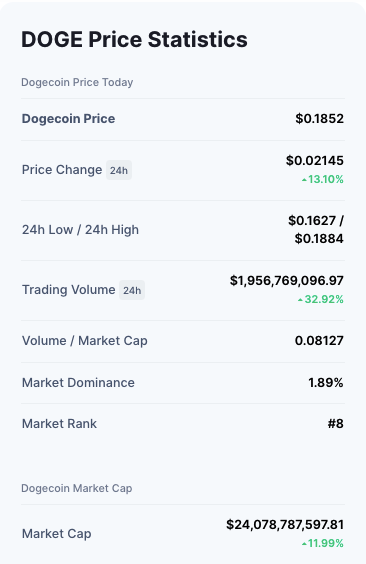
Dogecoin (DOGE)
- Dogecoin was created as a fun and unconventional payment system.
- The logo of Dogecoin is the face of the Shiba Inu dog from the “Doge” meme, reinforcing the “fun” concept behind DOGE
- Lauched in 2013, it quickly became a fan favourite
- Dogecoin’s block time is 1 minute as opposed to Litecoin’s 2.5 minutes.
KPI’s for Cryptocurrencies
Market Capitalisation
- Market capitalisation is a term that calculates and tracks a cryptocurrency’s market worth.
- This metric compares the current value of each coin to major conventional (fiat) currencies.
- It is determined by the current price * by the circulating supply.
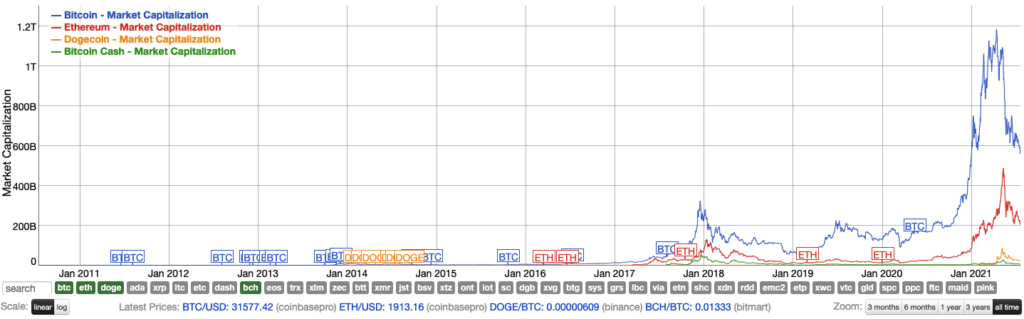
Print Date: 21st July 20210 – Source: Bitinfocharts.com
Volume (24h)
- The trading volume measures the number of coins that have been traded and/ or exchanged in that particular time period, usually 24hours.
- The 24-hour trading volume of a cryptocurrency refers to how much of a coin’s value has been bought and traded in a single day.
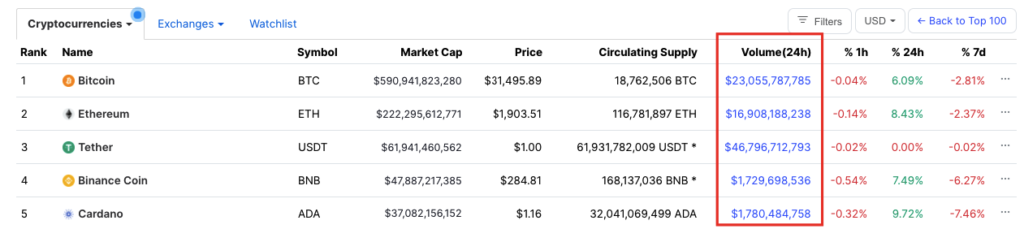
Print Date: 21st July 2021 – Source: Coinmarketcap.com
Transaction Volume
- Measures the number of transactions that have happened over time as well as the amount of coins involved in said transactions
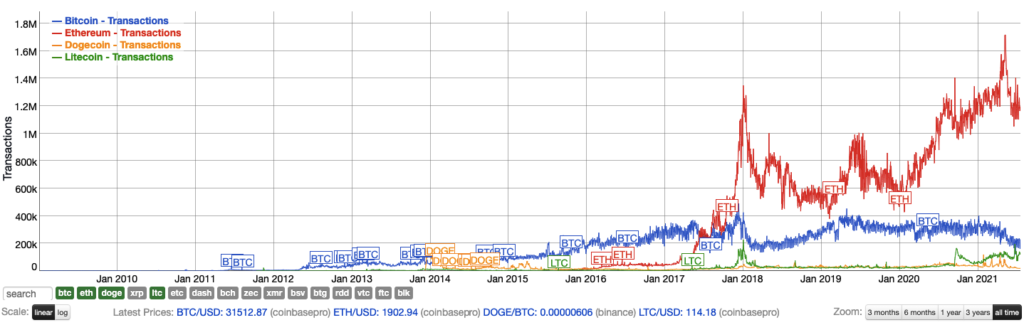
Print Date: 21st July 2021 – Source: Bitinfocharts.com
Exchange Rate
- The value of one currency in relation to another.
- An exchange rate is the rate at which one national currency is exchanged for another.
- Exchange rates can be fiat vs. fiat, crypto vs. fiat or crypto vs. crypto.
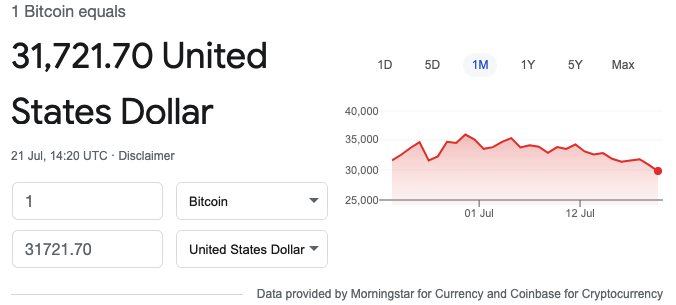
Print Date: 21st July 2021 – Source: Google
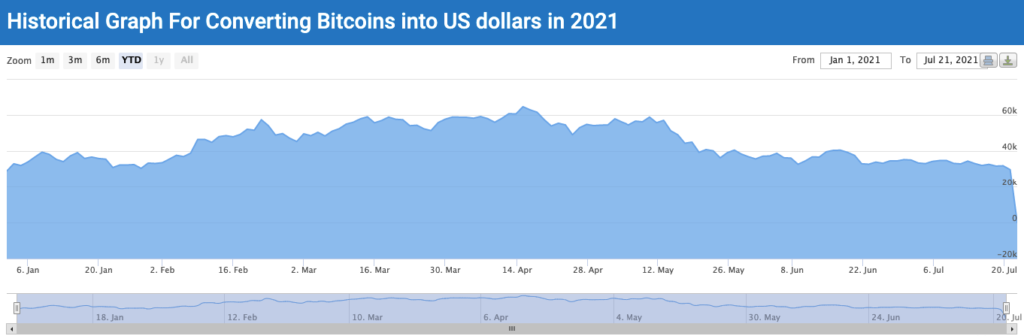
Print Date: 21st July 2021 – Source: Poundsterlinglive.com
Average Confirmation Time
- The average confirmation time, also known as block time, is the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed on the blockchain.
- The confirmation time of Bitcoin is about 10 minutes. Newer cryptocurrencies have a much lower block time.
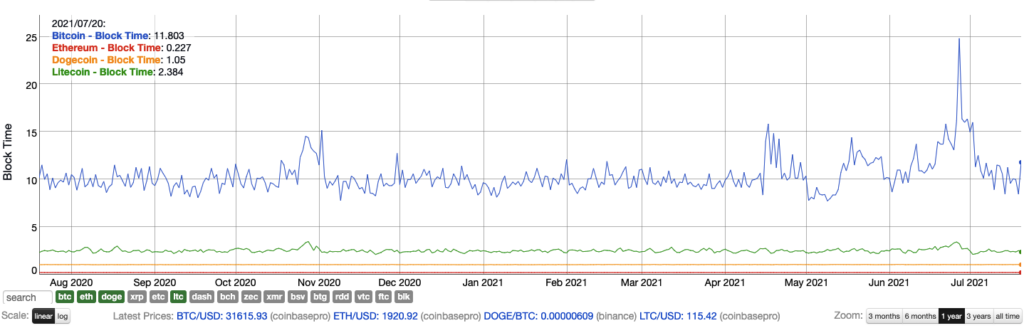
Print Date: 21st July – Source: Bitinfocharts.com
Network Hash Rates
- This metric is the network’s processing power.
- It gives an indication of the current difficulty in the mining process.
- Difficulty refers to the complexity to generate a SHA-256 hash for a candidate block.
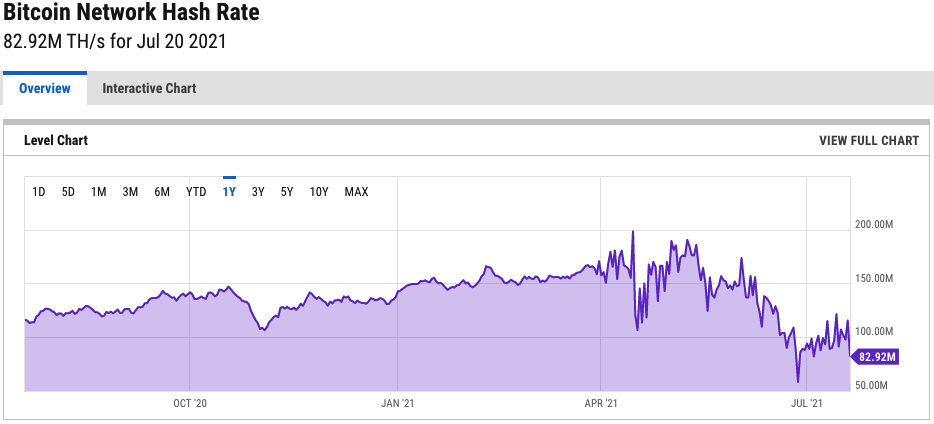
Print Date: 21st July – Source: Ycharts.com
Hashrate Distribution
- With the Hashrate Distribution you can identify the biggest mining pools and their contribution to the whole blockchain.
- This metric is never 100% accurate and it should only be used as a rough estimate.
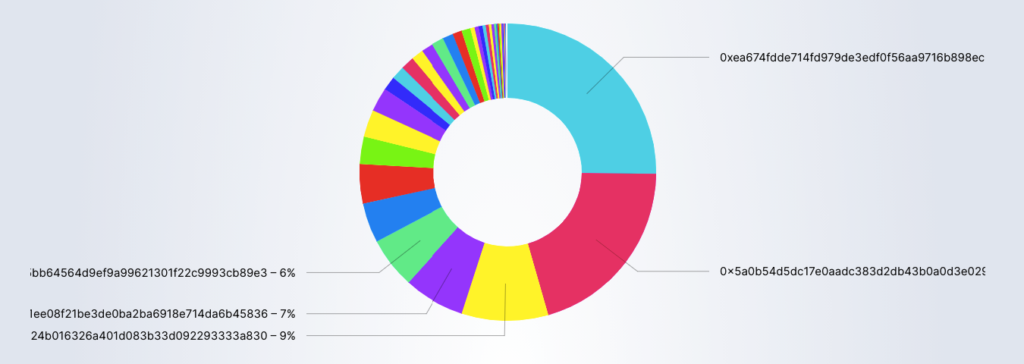
Print Date: 21st July – Source: Blockchair.com
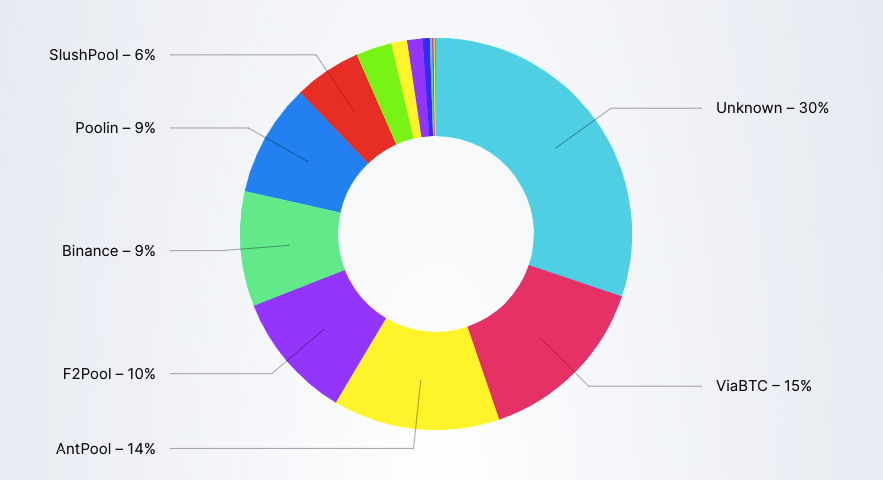
Print Date: 21st July – Source: Blockchair.com
Foundational Financial Services of Crypto
- The following are the basic components of cryptocurrency financial services:
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges
- Crypto Wallets
- Merchant Processing Services
- Once properly established and integrated, they will become the core of the payment system.
Crypto Exchanges
It’s an online marketplace where traders can buy and sell cryptocurrencies using fiat and/ or digital currencies.
Key Points
- A crypto currency exchange is an online platform where you can exchange and trade cryptocurrencies.
- It acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers, or to use crypto terminology, between a “maker” and a “taker.”
- A bitcoin or crypto exchange works like a stockbroker, you open an account and you can deposit money via bank transfer and other popular deposit methods.
- It works similarly to exchanging money at a bank or exchange bureau: you will pay a currency conversion fee and, in exchange, you will get your new currency.
How it Works
- The first step to start trading and exchanging cryptocurrencies is to open an account with a selected crypto exchange and pass the verification process.
- After this initial authentication process, verified users can fund their crypto exchange to start using the digital platform.
- You can deposit funds with different payment methods, check your exchange to see which ones are available for you.
- In order to withdraw funds, you can do so by choosing from one of the available payment methods.
Special Considerations
- Fees
- Some crypto exchanges might charge fund transfer fees, when making deposits and withdrawals. This also depends on the payment method chosen to transfer funds.
- In cases where your own currency is not accepted, you might have to pay conversion fees.
- As a general rule, most of the crypto exchanges have transaction fees, that apply after each completed buy and sell order.
- Important: Crypto exchange is NOT a crypto wallet.
- The crypto exchange is a trading platform, the crypto wallet is a digital storage service only.
- Most crypto exchanges also offer wallets, but they might charge a fee for this addition service.
Most Popular Crypto Exchanges
Crypto Wallets
A cryptocurrency wallet is a storage system that holds your public and/or public keys. It can be a physical device, digital program or paid online service.
A wallet is software that holds all your addresses. Use it to send bitcoins and manage your keys. […] A wallet is simply a collection of addresses and the keys that unlock the funds within.
Key Points
- Since cryptocurrencies are fully digital, you will never be able to hold a physical bitcoin or altcoin, so, in order to store them, you will need a private key.
- Crypto wallets don’t really store your cryptocurrencies; instead, they store your private key, which gives you access to all of them.
- There are 5 types of crypto wallets:
- Hardware wallets
- Paper wallets
- Desktop Wallets
- Mobile Wallets
- Web Wallets.
Hardware Wallets
- A physical piece of hardware that can be used to store your cryptocurrencies.
- Hardware wallets are also referred to as cold storage and non-custodial.
- It is the safest type of wallet as it’s an offline storage.
- You plug it to your computer when you need to manage your funds.
Paper Wallets
- A paper wallet is a printed version of your key, which contains the key itself and a QR code, which is used for transactions.
- It’s also an offline storage wallet, and, thus more secure than online options, but it’s also easy to loose and it an fade with time.
- It is now an outdated type of wallet.
Desktop Wallets
- Desktop wallets are installed on your computer, need internet access and provide control over you wallet from your device.
- They work as an address for the user to send and receive crypto.
- You can also store your private key.
Mobile Wallets
- Mobile wallets or wallet apps, are wallets downloadable on your mobile phone.
- Most desktop and online wallets come with the mobile app as well.
- Some crypto exchanges include a mobile wallet, and vice-versa.
- Since it’s an online platform, it’s a custodial wallet and hot storage.
Online/ Web Wallets
- With online wallets, you don’t need to download any software to your computer or phone, meaning you can connect anywhere, anytime.
- Unfortunately, the main drawback is that it’s more vulnerable to hacking, than other wallets.
Cold vs Hot Storage
Cold Storage
- It is disconnected from the internet, completely offline, making it the safest crypto wallets.
- Cold storage wallets include: Hardware wallets (physical devices, like a pen drive) and paper wallets.
Hot Storage
- Hot wallets are the best option if you’re currently trading or exchanging crypto.
- Connected to the internet
- Hot wallets are vulnerable to online hacking, change in regulations and technical difficulties.
Custodial vs Non-Custodial
Custodial
- A custodial wallet keeps your private keys and digital assets safe, meaning you can always recover. It offers a backup.
- If you lose your private key, you can always recover it.
- It offers, for most parts, free and instant transactions.
Non-Custodial
- Non-Custodial wallets means that no one else, except you, own your private key.
- It is the safest way of owning crypto, since it’s not connected to the internet, it’s safe from external cyber attacks.
- But a los wallet, also means total loss of your funds and crypto.
- Non-custodial wallets are cold storage, like hardware and paper wallets.
Merchant Processors
Merchant processors allow business to accept cryptocurrencies as payment method.
Key Points
- They are the equivalent to fiat currency merchant processors (First Pay, WorldPay, Elavon, Authorize.net, Square, etc) for the most popular payment methods (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc).
- They include the integration into the business’ website and shopping cart, and the conversion into legal tender after the purchase.
- Common payment systems use a “pull” mechanism, in which they take funds from your account and route them via a vast and complicated network.
- With bitcoin payments it’s different, as only two parties have access to the transaction and only at the time that it’s being made. This is called a “push” mechanism.
Likely Initial Areas For Adoption
- Online Products: affordable merchant fees for vendors
- Sensitive Products: HIV tests, pregnancy tests, pornography, etc.
- High-Risk Vendors: giving access to their credit card/credit line to “risky” vendors.
- International Customers: chargeback frauds are avoided due to the irreversible nature of cryptocurrency transactions.
- Open Bazaar : It’s a peer to peer e-commerce application, that it’s expected to grow in popularity paving the way for similar e-commerce sites.